1. Introduction
To describe the behaviour of fluid flow in a single term, Osborne Reynolds, a British engineer, introduced a dimensionless quantity known as the Reynolds Number. It helps in identifying whether the flow is laminar, transitional, or turbulent.
The Reynolds Number relates the effect of inertia and viscosity of a fluid to determine the nature of its flow. It plays a key role in studying pipe flow, open channel flow, and many engineering applications.
In this article, we will discuss the definition, formula, flow classification, and significance of the Reynolds Number in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
Definition of Reynolds Number
The Reynolds Number (Re) is a dimensionless quantity that helps to predict the type of flow of a fluid. It is defined as the ratio of inertia force to viscous force present in the flowing fluid, as given in the formula below:
In simple words, it tells us which force is dominating in the flow:
- If viscous forces are stronger → the flow is laminar (smooth).
- If inertia forces are stronger → the flow becomes turbulent (irregular).
Thus, it acts as a measuring scale for identifying the nature of the flow, whether it is smooth or mixed.
Mathematical Expression of Reynolds Number
The mathematical expression of the Reynolds Number is given by:
Where,
- Re = Reynolds Number (unitless and dimensionless)
- ρ = Density of fluid (kg/m³)
- V = Velocity of fluid (m/s)
- D = Characteristic length or diameter of pipe (m)
- μ = Dynamic viscosity of fluid (N·s/m²)
- ν = Kinematic viscosity of fluid (m²/s)
Since both inertia and viscous forces have the same dimensions. So, the Reynolds Nos has no unit, which is why it is called a dimensionless number.
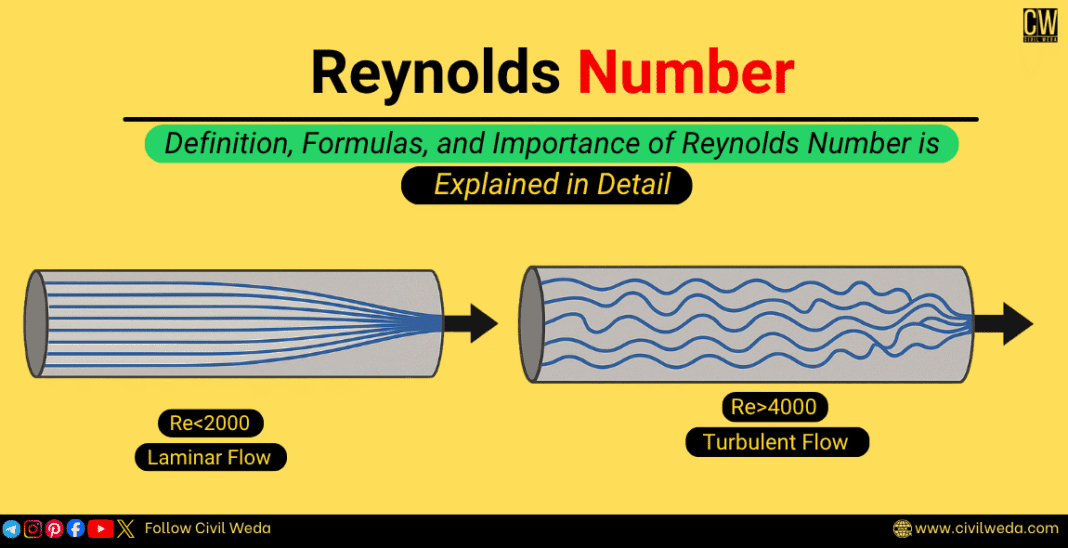
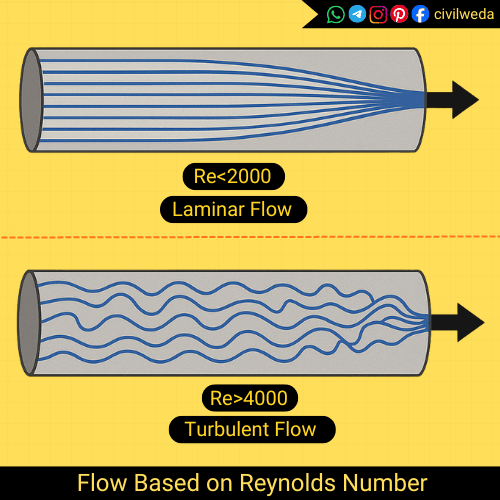
Classification of Flow Based on Reynolds Number
The type of flow of a fluid mainly depends on the value of the Reynolds No. According to Osborne Reynolds’ experiments, the flow of fluid can be classified into three main types, which are given as:
In the case of Pipe Flow
In the case of pipe flow, the classification of flow based on the Reynolds number is given in the table below:
| Type of Flow | Range of Reynolds Number (Re) | Nature of Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Laminar Flow | Re < 2000 | Fluid particles move in smooth, parallel layers |
| Transitional Flow | 2000 ≤ Re ≤ 4000 | Flow changes from smooth to irregular |
| Turbulent Flow | Re > 4000 | Flow becomes random, mixed, and unstable |
In the case of Open Channel Flow
In the case of Open Channel Flow, the classification of flow based on the Reynolds No is given in the table below:
| Type of Flow | Range of Reynolds Number (Re) | Nature of Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Laminar Flow | Re < 500 | Flow is smooth and well-ordered |
| Transitional Flow | 500 ≤ Re ≤ 2000 | Flow starts to fluctuate slightly |
| Turbulent Flow | Re > 2000 | The flow starts to fluctuate slightly |
Significance and Importance of Reynolds Number
The Reynolds Number is one of the most useful and practical parameters in fluid mechanics.
It helps engineers and researchers understand how a fluid will behave under different conditions of velocity, viscosity, and pipe size.
Here are some key points that show its importance
1. Determines the Type of Flow
The Reynolds No helps to identify whether the flow is laminar, turbulent, or transitional. This is very important in the design of pipelines and hydraulic structures, as the energy losses depend on the nature of the flow.
2. Helps in Choosing the Right Formula
Different flow conditions require different equations.
For example:
- Laminar flow → Hagen–Poiseuille equation is used.
- Turbulent flow → Darcy–Weisbach equation is used.
So, before solving any fluid problem, engineers first check the value of the Reynolds Number.
3. Used in Model Studies
In hydraulic model studies (like dam spillways, river flow, etc.), dynamic similarity between the model and prototype is achieved using the same Reynolds No.
This ensures the model behaves like the real system.
4. Helps in Designing Hydraulic Systems
When designing pipes, valves, or pumps, the Reynolds No helps predict frictional losses and pressure drops. It ensures that the system is both efficient and economical.
5. Indicates Flow Stability
A lower Reynolds Number means the flow is stable and smooth, while a higher value shows that the flow is unstable and mixed.
Thus, it also gives an idea about the flow stability.
In Short, Reynolds Number acts as a “flow indicator”; it helps engineers understand, predict, and control how a fluid will behave in real-life conditions.
Read more Civil Engg Topics
- Viscosity
- Atterberg Limits
- Compass Survey
- Factors affecting per capita demand
- Drip Irrigation
- Timber
- Seasoning of Timber
- Types of soil
Conclusion
The Reynolds Number is one of the most important concepts in fluid mechanics.
It helps to understand how a fluid behaves while flowing through a pipe or over a surface. By using this single dimensionless number, engineers can easily identify whether the flow is laminar, transitional, or turbulent.
1. What are the units of Reynolds Number?
Reynolds Number has no unit, so it is a dimensionless quantity.
2. Why is Reynolds Number important in fluid mechanics?
It helps engineers to predict the nature of flow, determine energy losses, and design efficient hydraulic systems.
3. Who introduced the Reynolds Number?
It was introduced by Osborne Reynolds, a British engineer, to describe the flow behaviour of fluids.
Thank You for Reading! 🙏
We hope this article helped you clearly understand the Reynolds Number in civil engineering. If you found this complete article useful, please share it with your friends and university students. For more informative posts on civil engineering topics, stay connected with Civil Weda. 🚀