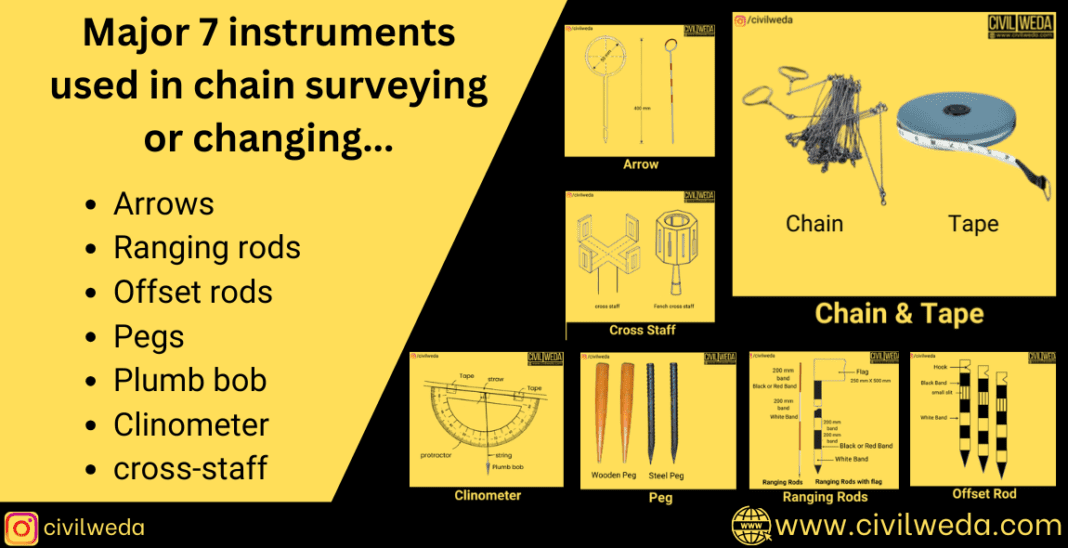
Introduction:
Hey Learner, No doubt in chain surveying, obviously, a chain or tape is required, but apart from the chain or tape, some additional instruments are used in chain surveying, such as Arrows, ranging rods, Offset rods, Pegs, Plumb bob, Clinometer, cross-staff, etc. In this post, we will discuss the 7 major instruments used in Chain surveying. Let’s get started.
Arrow
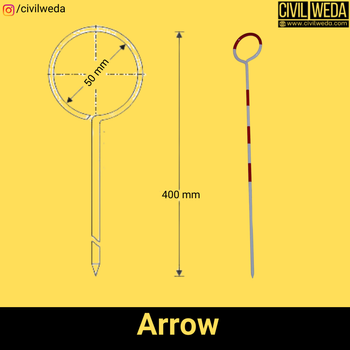
The arrow is the instrument used in chain surveying to mark the end position of the chain or tape on the ground surface Arrow is made of good quality hard-tempered steel wire of 4 mm diameter. Generally, at least 10 arrows are supplied with a single chain. The length of the Arrows varies between 25 cm to 50 cm.
As per IS:1842, the overall length of the arrow is 40 cm, with a 5 cm diameter loop. One end of an arrow is sharp, and the other end of the Arrow is bent into a loop of 5 cm diameter, as shown in the figure.
Advantages of Arrow:
Arrows are used to record the number of chain lengths or tape lengths which is already been laid during measuring the survey line.
Ranging rod
Ranging rods are the instruments used in chain surveying, which are used to locate intermediate points such that this point lies on the straight line joining the two end stations.
Ranging rods are generally used for ranging of two points on the ground. A ranging rod is required in cases where the length of the chain and tape is small compared to the distance between the two survey stations.
Ranging rods are made from well-seasoned timber with a 30 mm nominal diameter.
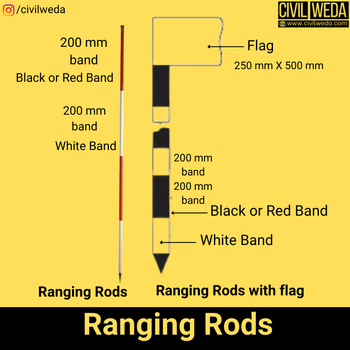
As per IS 2288, ranging rods are available in 2 m long length and 3 m lengths. 2 m long length ranging rods are available with 10 bands of 200 mm each and 3 m long length ranging rods with 15 bands each of 200 mm length. These bands are painted black and white alternatively to make them clear and visible for long distances.
When the distance is very large, then flags of red and white colour or sometimes yellow and white colour of size 250 mm x 500 mm are used, which are attached at the top of the ranging rod as shown in the figure.
The bottom of the ranging rod is fitted with a hollow cast iron or steel sheet so that its end does not wear easily.
The shapes of the ranging rod are circular or octagonal in cross-section and diameter of 30 mm generally.
Ranging poles
Ranging poles are instruments used in chain surveying. It is similar to ranging rods, but ranging poles are longer and greater in diameter than ranging rods, and they are used in cases of very long survey lines. The length of the ranging poles varies from 4 m to 8 m, and the diameter from 60 mm to 100 mm. Provided greater stability as compared to the ranging rods
Offset rods
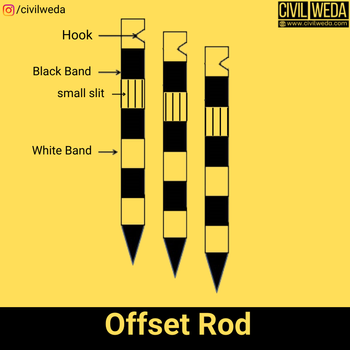
Offset rods are similar to ranging rods, but it is provided with short slots passing through the section of the rod, just like in a cross-staff. These slots are made at a right angle to each other.
An offset rod is an instrument used in chain surveying which used to measure the offset line, which is at a right angle to the survey line. The length of the offset rod is usually 3m and is provided with a steel shoe at one end of the offset rod.
With the help of the offset rod, offset lines are aligned at a right angle to the survey line by looking through two slots. A typical diagram of an offset rod. As shown in the figure.
Pegs

Pegs are instruments used in chain surveying, which are used to mark the survey station and end point of survey lines on the ground. These pegs are also used to mark the intersection of lines and other such points, which are more or less permanent.
Pegs are generally made of wood with a square section and tapered at one end. The sizes of pages are 25mm X 25mm X 150mm and 40mm X 40mm X 400mm long. The pegs are driven into the ground using a mallet with about 40 mm length projecting one above the ground. A nail is driven into the peg to mark the exact location of the station.
For a very hard stratum, instead of wooden pegs, steel dowels of about 10 mm diameter are used. As shown in the figure
Plumb Bob:
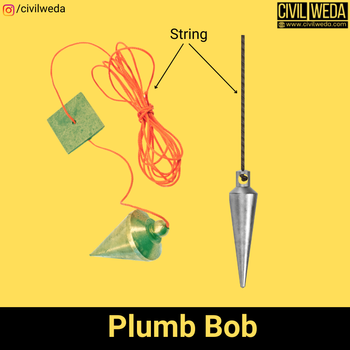
A freely suspended plumb bob always aligns itself in the direction of gravity and points towards the centre of the Earth. It indicates whether a line is truly vertical or not.
Plumb Bob is an instrument used in chain surveying which used to place the tape directly over a point when a tape or a chain is suspended over it. These are also used to transfer the point on the tape to the ground (generally in the case of sloping ground). In surveying plumb bob is mainly used to centring instruments like a magnetic compass, theodolite, plane table, etc.
Plumb Bob is made up of bronze or brass in the shape of an inverted cone, and a hook is provided at the top of the plumb Bob to attach a string. The weight of the Plumb Bob varies from 2 Newton to 5 Newton, and the length of the Plumb Bob is about 50 mm. As shown in the figure.
Cross staff
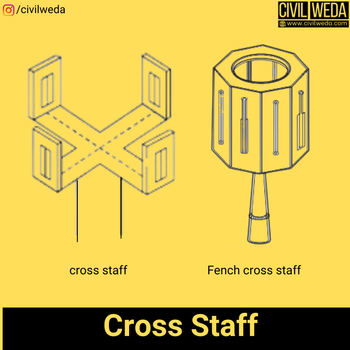
The cross-staff is the instrument used in the chain survey for setting out the offsets to the chain line from the given point. The cross-staff is also used for setting out a right angle on the ground. For very high accuracy demanding work, a theodolite is used to lay out a right angle to the chain line. As shown in the figure
Clinometer
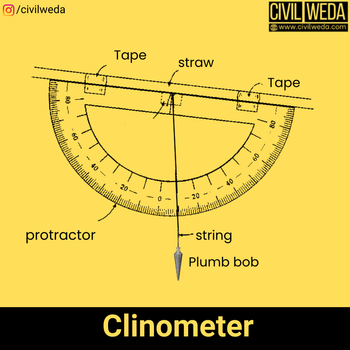
The clinometer is the instrument used in chain surveys for measuring the slope of the ground. It consists of a graduated protector with a pinhole at the eye vane. A plum Bob is suspended from the centre of the protector. When the ground surface is horizontal, then the plumb bob marks zero reading, and when the ground surface is sloping, the plumb Bob marks the corresponding reading and gives the slope of the ground. A typical diagram of a clinometer is shown in figure Clinometer is on in figure.
Read our other articles on Surveying and Building Materials to boost your civil knowledge!
- Types of bearings in surveying
- Compass survey
- Topographic survey
- Timber used in construction
- Bitumen concrete
Conclusion:
In chain surveying, accurate measurement of distances and angles depends not only on the chain or tape but also on the proper use of several supporting instruments. Each instrument, such as the arrows, ranging rods, offset rods, pegs, plumb bob, cross-staff, and clinometer, plays an important role in ensuring precision and efficiency during the survey.
These instruments help in marking points, aligning lines, measuring offsets, and maintaining verticality on the ground. Therefore, a good understanding and correct handling of these tools are essential for every civil engineer or surveyor to achieve reliable and error-free results in chain surveying.
FAQs on Chain Surveying
1. What are the main instruments used in chain surveying?
The main instruments are Arrows, Ranging Rods, Offset Rods, Pegs, Plumb Bob, Cross-Staff, and Clinometer etc.
2. What is the use of an Arrow in chain surveying?
An Arrow is used to mark the end position of a chain or tape on the ground during measurement.
3. Why are ranging rods used in surveying?
Ranging rods are used to align and mark points in a straight line between two survey stations.
4. What is the function of a Plumb Bob in chain survey?
A Plumb Bob helps in ensuring that a point on the tape or chain is exactly above a ground point.
5. What is the purpose of a Cross-Staff?
A Cross-Staff is used to set out right angles or measure offsets at 90° to the survey line.
Thank You for Reading! 🙏
We hope this article helped you clearly understand the instruments used in chain surveying in civil engineering. If you found this complete article useful, please share it with your friends and university students. For more informative posts on civil engineering topics, stay connected with Civil Weda. 🚀