Introduction

Water plays a vital role in daily human activities, and its requirement is never the same for all regions. In civil engineering, the term per capita demand of water is used to define the average quantity of water consumed by a person in one day. This value is generally expressed in litres per capita per day (LPCD).
The purposes of planning of water supply system. In India, the standard value of 135 litres per capita per day (LPCD) is adopted for urban water supply schemes, as recommended in the Bureau of Indian Standards – IS 1172 Code. Still, this demand can vary widely depending on different conditions such as climate, city population, living standards, quality of supply, and public or industrial usage. Understanding these influencing factors is important for engineers and planners because it ensures proper design, efficient management, and sustainable distribution of water resources.
Per capita demand for water
Per capita demand of water is the annual average amount of daily water required by one person, and it includes the domestic uses, industrial uses and commercial uses, public uses, waste, and theft of water, etc. In addition to per capita water demand, water demand is studied in various categories, such as domestic, commercial, and industrial needs. To learn more about various types of water demand, check our detailed post on Water Demand.
Factors Affecting Per Capita Demand of Water
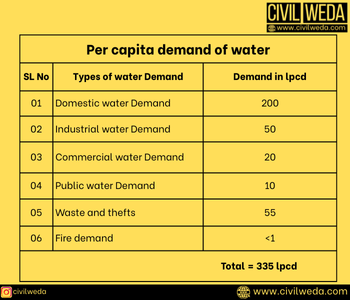
The annual average demand for water varies considerably from different town or city to another. This figure generally ranges between 100 to 360 lpcd for Indian conditions. The variation in per capita water consumption of different cities or towns depends upon various factors, which must be thoroughly studied and analysed before fixing the per capita demand for design purposes. These factors are discussed below.
There are various factors listed below that affect the per capita demand of water.
Size of the City or Town
The total water demand depends on the size of the population, and for the design of the water supply scheme for a given population size following guidelines may be adopted.
Climate Condition
In hotter and drier places, per capita demand of water is generally more because more of the bathing, clearing, air cooling, and air conditioning at ac are involved. Similarly, in extremely cold countries, more water may be consumed to open the tap to avoid freezing of pipes, and there may be more leakage from pipe joints since metals contract with cold.
Quality of Water Supplies

If the quality and test of supplied water is good, it will be consumed more water because, in that case, people will not use other sources such as private hand pumps, and it increases the per capita demand of water. Similarly, certain industries, such as boilers that require standard quality water, will not develop their own supplies and will use public supplies, provided the supplied water is up to their required standard. In that case per capita demand of water will also increase.
Pressure in the Distribution System.
If the pressure of water in the distribution pipes is high and sufficient to make the water recess at the third or even 4th story building, per capita water consumption will definitely be more. Per capita water demand increased because of two reasons, which are given below-
- The people living in the upper storage will use water freely, as compared to the case when water is available to them
- The losses and wastage due to leakage are considerably increased if their pressure is high
Read more Civil Engg Topics
- Chlorination of water
- Types of Water Demand
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Sprinkler Irrigation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Irrigation
- Drip Irrigation
- Viscosity
- Surface Tension
Conclusion
In civil engineering, understanding the per capita demand of water is very important for designing an efficient and sustainable water supply system. Although the standard value of 135 LPCD is generally adopted in India, the actual demand may change depending on factors such as climate, city size, lifestyle, and the quality of the supply system. These variations highlight the need for proper planning and resource management. For students, this topic is not only a part of academic studies but also a practical concept used in real-life projects. By considering the influencing factors carefully, engineers and planners can ensure that water resources are used wisely and distributed fairly to meet the growing needs of the population.
FAQs on Per Capita Water Demand
1. How is per capita water demand calculated?
Per capita water demand is calculated by dividing the total daily water consumption of a community or city by its total population. The result is expressed in litres per capita per day (LPCD).
2. What is the standard per capita demand of water in India?
As per CPHEEO norms, the standard per capita demand of water in Indian urban areas is taken as 135 LPCD. This value is used for planning water supply schemes.
3. Which factors affect the per capita demand of water?
The main factors include climate, city size, living standards, cost and quality of supply, industrial and commercial activities, and distribution system pressure.
4. Why is per capita water demand important in civil engineering?
It is important because it helps engineers and planners design efficient water supply systems, ensuring that the needs of the population are met without wastage.
5. Does the per capita demand of water vary from place to place?
Yes, it varies depending on local conditions. For example, hot and dry regions need more water, while cold regions or small towns may have a lower per capita demand.
Thank You for Reading! 🙏
We hope this article helped you clearly understand the per capita demand of water in civil engineering. If you found this complete article useful, please share it with your friends and university students. For more informative posts on civil engineering topics, stay connected with Civil Weda. 🚀


