Introduction
In modern construction, time, quality, and efficiency play a crucial role. To meet these requirements, Ready Mix Concrete (RMC) has become one of the most widely used materials. Instead of mixing concrete at the site with uncertain quality, RMC is manufactured in a batching plant under strict quality control and delivered to the site using transit mixer trucks.
This article explains what Ready Mix Concrete is, its ingredients, types, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and its comparison with site-mixed concrete.

History of Ready Mix Concrete
The exact beginning of Ready Mix Concrete (RMC) is not clearly documented, and different sources mention different timelines. Some reports suggest that the first use of ready-mixed concrete dates back to 1913 in Baltimore, USA where concrete was mixed in a central plant and delivered to construction sites. According to Wikipedia – Ready Mix Concrete By the late 1920s, especially around 1929, more than 100 batching plants were already operating in the United States.
However, the large-scale adoption of RMC was relatively slow in the early years due to limitations in transportation, mixing equipment, and handling techniques. It was only after the 1960s that the industry started expanding rapidly, supported by advancements in transit mixers, batching technology, and construction demands. Since then, Ready Mix Concrete has continued to grow worldwide, and today it is considered an essential material for modern infrastructure development.
What is Ready Mix Concrete?
Ready Mix Concrete (RMC) is a type of concrete that is manufactured in a central batching plant by accurately mixing cement, sand, aggregates, water, and admixtures in a controlled environment. After mixing, it is transported to the construction site in special trucks known as transit mixers, which continuously rotate to prevent the concrete from setting.
👉 In simple words, RMC is factory-made concrete delivered to the site in ready-to-use form.
Ingredients of Ready Mix Concrete
The following materials are used in RMC:
- Cement – Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC), or Portland Slag Cement (PSC).
- Fine Aggregate – Clean river sand or manufactured sand (M-Sand).
- Coarse Aggregate – Crushed stone or gravel of specified sizes.
- Water – Clean potable water as per IS 456 standards.
- Admixtures – Plasticizers, superplasticizers, retarders, accelerators, etc., to improve workability and setting time.
Types of Ready Mix Concrete
Based on the method of mixing and transportation, RMC is divided into three main types:
- Transit Mixed Concrete
- Mixing is done inside the transit truck.
- Suitable for small to medium projects.
- Mixing is done inside the transit truck.
- Shrink Mixed Concrete
- Partially mixed at the plant and completed at the site.
- Saves time and reduces load on the mixer.
- Partially mixed at the plant and completed at the site.
- Central Mixed Concrete
- Completely mixed in the batching plant before transportation.
- Ensures the highest quality and consistency.
- Completely mixed in the batching plant before transportation.
Manufacturing Process of Ready-mix Concrete
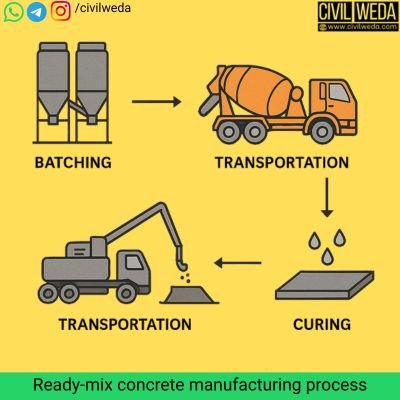
- Batching – Accurate measurement of ingredients using automated systems. While batching RMC, the moisture present in fine aggregates like sand directly affects the weight and volume measurements. If this bulking of sand is not considered, the mix may become weaker or consume more cement. To understand this effect in detail, read our complete guide on Bulking of Sand.
- Mixing – Ingredients are mixed in the batching plant (central or partially).
- Transportation – Transit mixer trucks carry the concrete to the site.
- Placing & Compaction – Concrete is poured at the site and compacted using vibrators.
- Curing – Proper curing ensures the development of strength and durability.
Transportation of Ready-Mixed Concrete
Once Ready Mix Concrete is manufactured in a batching plant, it must be transported quickly and efficiently to the construction site. The quality of RMC depends not only on its production but also on how it is delivered.
In India, the transportation and quality requirements of RMC are guided by IS 4926:2003, which specifies standards for ready-mixed concrete. You can check and download to the official document on the Bureau of Indian Standards website
Methods of Transportation of Ready-mixed Concrete
- Transit Mixer (Truck Mixer)
- Most common method.
- Concrete is continuously agitated while being transported.
- Capacity: 4–7 cubic meters.
- Prevents segregation and maintains workability.
- Agitator Truck
- Used for shorter distances.
- Has a rotating drum to keep concrete in motion.
- Dump Truck (Non-agitating trucks)
- Used when site is very near to the batching plant.
- Not suitable for long distances as concrete may segregate.
- Pumps & Pipelines
- For high-rise buildings or difficult-to-reach areas.
- Concrete is pumped vertically or horizontally.
Ensure Quality During Transport
- Concrete must be placed within 90 minutes of mixing.
- Continuous rotation of drum is necessary to avoid segregation.
- Avoid delays in traffic or at the site.
- Retarders or admixtures can be added for long-distance transport.
Advantages of Ready Mix Concrete
High Quality and Uniformity – Automated batching ensures accurate mix proportions.
Time-Saving – No site mixing, concrete is ready to use.
Less Wastage – Precise material usage reduces wastage.
Space Saving – No need to store cement, sand, or aggregates at the site.
Better Workability – Use of admixtures improves performance.
Suitable for Large Projects – Ideal for high-rise buildings, bridges, and highways.
Disadvantages of Ready Mix Concrete
High Initial Cost – Plant setup and transportation costs are high.
Transit Time Issues – Delays may cause premature setting.
Not Suitable for Remote Areas – Transportation to far-off sites is difficult.
Strict Quality Control Needed – Any error in batching affects final strength.
Applications of Ready Mix Concrete
RMC is widely used in such way:

- High-rise buildings and residential projects
- Bridges, flyovers, and dams
- Roads and highways
- Commercial complexes and industrial structures
- Metro projects and airport runways
RMC is widely used in high-rise buildings, roads, bridges, and dams. In the same way Geopolymer Concrete is increasingly being adopted for sustainable and eco-friendly construction projects.
Difference Between Site-Mixed Concrete and Ready Mix Concrete
| Feature | Site-Mixed Concrete | Ready Mix Concrete |
| Mixing Location | At the construction site | At the batching plant |
| Quality Control | Low, depends on labor | High, automated |
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Material Wastage | More | Very less |
| Storage Space | Required at the site | Not required |
| Cost | Economical for small works | Better for large projects |
Future of Ready Mix Concrete:
With the increasing demand for smart cities, sustainable infrastructure, and high-rise construction, the use of RMC is expected to grow rapidly. Modern developments such as self-compacting concrete, fiber-reinforced concrete, and green concrete are often prepared using RMC plants, making them the backbone of the future construction industry.
Read more Civil Engg topics
- Chlorination of water
- Per Capita Water Demand
- Pile foundation
- Drip Irrigation
- Instrument used in a chain survey
- Fillet Weld
- Bulking of sand
Conclusion
Ready Mix Concrete has transformed the construction industry by offering high-quality, time-saving, and reliable concrete. Although it requires proper planning and quality control, its advantages far outweigh the disadvantages. With the rapid growth of infrastructure and smart cities, the demand for RMC will continue to increase in the coming years
FAQs on Ready Mix Concrete
1. What is Ready Mix Concrete (RMC)?
Ready Mix Concrete is a type of concrete that is manufactured in a batching plant under controlled conditions and delivered to the construction site in a ready-to-use form using transit mixer trucks.
2. What are the main advantages of Ready Mix Concrete?
RMC provides high quality, uniformity, and strength. It saves time, reduces wastage, requires less storage space, and is ideal for large-scale projects like high-rise buildings, highways, and bridges
3. Is Ready Mix Concrete more expensive than site-mixed concrete?
Initially, RMC may seem costlier due to plant and transportation charges. However, for large projects, it becomes economical because of reduced wastage, faster work, and better durability.
4. What is the difference between site-mixed concrete and RMC?
Site-mixed concrete is prepared manually at the construction site with varying quality, while RMC is manufactured in a batching plant with strict quality control and then transported to the site in ready-to-use condition.
5. Which IS Code is followed for Ready Mix Concrete in India?
In India, IS 4926:2003 specifies the requirements for Ready Mix Concrete. Additionally, IS 456:2000 provides general guidelines for plain and reinforced concrete works.
Thank You for Reading! 🙏
We hope this article helped you clearly understand the Ready Mix Concrete in civil engineering. If you found this complete article useful, please share it with your friends and university students. For more informative posts on civil engineering topics, stay connected with Civil Weda. 🚀


